Designing for FoodBasket
Hear me rant about the process of designing my capstone project, while people that have no clues about actual designs scream at me for not doing it well enough.
Registering and Logging in with user accounts, along with session tokens for authorization stored in HTTP cookies, made possible with CORS (CORS is a pain).
Published on Dec 5, 2024
Updated on Dec 5, 2024
Check out previous chapter: Chapter 1. Setting up the server. This article is a continuation of my development process on Lubook.
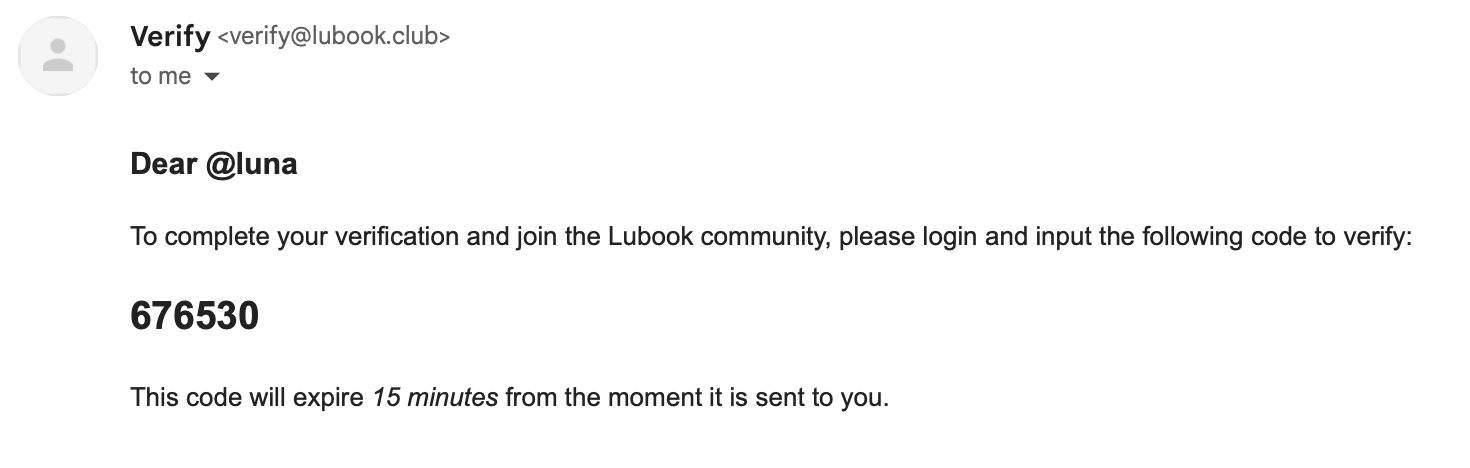
To even start seeing anything on the frontend, a user account and basic authentication is pretty much needed to use everything the app has to offer. But I just realized something difficult, at first, it was just a generic username-based account system, but then I would like to allow the changing of the username handles, since the primary key is the PSQL serial, not the username. I also designed a form to allow for email inputs also, with a simple email verification.
The problem is, I don’t know how to make email verification. I didn’t setup the database to do that either, yet the design files have it (wow, me to blame, I made that design file) and I feel like it might be a good idea to keep and learn this, instead of removing it. But that also comes up with a new problem, what about testing? That means another issue to mock since we can’t just create email servers to catch if the email gets sent correctly?
After reading a bunch of articles and wikis, I think the best route would be to use nodemailer, and utilize SMTP or IMAP to send simple HTML based emails. Two problems:
The worst thing is, I can’t keep paying for more services as a solo developer on this project. I’m still a uni student with pretty limited funds living in SEA, so American-affordable prices aren’t really affordable for me. I’m already paying for a VPS instance for DB/Express, a domain and a S3 storage for images hosting. If this keeps going, it doesn’t seem viable for me at all.
I think I might have to go with PurelyMail that offers a SMTP email address with custom domains, for around $10 a year, compared to that, Google Workspace charges $6 per month, albeit with a larger storage.
Setting up the email sending is pretty simple and straight forward with Nodemailer. Here’s the result code, in case you need this later:
export const emailTransport = createTransport({
host: "smtp.purelymail.com",
port: 465,
secure: true, // port 465 is SMTPS, put false if not 465
auth: {
user: "verify@lubook.club",
pass: process.env.EMAIL_PASSWORD, // Of course don't expose this lol
},
});
export async function sendVerificationEmail(
id: number,
name: string,
email: string,
) {
// SQL stuff...
await emailTransport.sendMail({
from: "Verify <verify@lubook.club>", // Google forces you to identify yourself as the same email as you authenticated as. If not, you can't send to gmail accounts.
to: email,
subject: "Lubook Verification",
text: "text version if html can't display",
html: "html version",
});
}
After registering the user should be able to verify themselves and sign in, right? We’re using HTTP cookies, with a token signed by JWT, pretty standard and “default” enough right. The problem is also, I have never done anything related to cookies. Knowing how annoying CORS is, this will be very frustrating to figure out. Since the API server sits on api.lubook.club and the web server sits on lubook.club, that’s a CORS (Cross Origin Resource Sharing) request.
What is even worse? When you do development, the server you want to deal with is localhost:4321 for the frontend and localhost:8080 for the backend. Due to some weird issues with browsers handling cookies around localhost and URLs with ports, setting up the development environment is not straight forward. Like the one quote I saw on StackOverflow, it’s always CORS, the problem is always CORS.
I have setup CORS on the express server, allowing http://localhost:4321 (which is Astro’s URL), and setup mode: 'cors' on the client’s fetch request. Doesn’t work. For some reason?
If I use curl to check, the header Access-Control-Allow-Origin: http://localhost:4321 is set correctly. Theoretically, this should allow the Astro page to connect and request for data, yet it just doesn’t work? It just crashes right away, and fetch doesn’t even go through.
㊗ Oh my gosh! It was because the allow origin allowed http://localhost:4321/ (with a slash) and the web server is on http://localhost:4321. How stingy do you have to be??
Setup CORS on the server-side:
app.use(
cors({
origin: process.env.CORS_ORIGIN,
credentials: true,
allowedHeaders: "Origin,X-Requested-By,Content-Type,Accepts",
}),
);
app.options("*", cors());Of course, CORS_ORIGIN is an environment variable that points to the URL of your WEB SERVER, down to every single letter. For my case, it would be https://lubook.club. I have to make sure www.lubook.club redirects back to the root domain, or CORS wouldn’t allow it; The allowed headers is to make sure that valid headers are accepted by CORS instead of it dropping it entirely.
The last line, setting up OPTIONS http verb because some browsers like late Chrome (I think?) and Safari sends an OPTIONS request before the actual fetch happens, and if that request fails, the fetch might not happen entirely.
For the client-side, I’m pretty sure CORS is the default mode, but I marked mode: "cors" in fetch requests anyway:
return await fetch(URL, {
method: METHOD,
mode: "cors", // Just for the peace of mind
headers: {
"Content-Type": "application/json",
},
redirect: "follow",
body: JSON.stringify({ profile, password }),
credentials: "include", // Make sure for cross-site cookies
});
Loading the Astro page now shows an authenticated request, with proper accounts and usernames.
Another part that I thought would be super simple turns out to have a problem again, Frontend Testing. I have done frontend testing on various applications before, the only difference is, this time, frontend has fetch requests to check for backend data, this is the problem.
The solution that I seem to gather from stackoverflow answers is to replace the fetch function right away:
const fetchMock = vi.fn(
async (url, options) => new Response(new Blob(), { status: 200 }),
);
global.fetch = fetchMock;The problem?
ReferenceError: global is not definedSeems to be that it doesn’t work on Vitest since that runs on Vite, and Jest ran primarily on Webpack and that included the global variable.
The solution I found is to intercept fetch on its own, do a vi.stubGlobal("fetch", mockFn).
After registering, the app is supposed to redirect the user back to login page. But window.location.href changing would be detrimental to the browser testing mode. We need a way to intercept this call.
I have gathered a lot of information around the internet, to see what works and what doesn’t. I think the problem is that I use Vitest + Playwright + TypeScript, which a lot of solutions seem to use Jest + JSDOM + JavaScript, funnily as opposite as it can get.
What doesn’t work:
location with Object.defineProperty.href.vi.spyOn the set function of window.location.href.vi.spyOn the assign function of window.location.window.location with window.location = something.What worked: to not interfere with other tests, I put the one test that works on window.location.href on another test file. I also put the href assignment in another synchronous function in a utils file of some sort, we’re gonna mock the utils file instead, since Vitest Browser Mode is in beta and there’s not enough exposed library like Playwright.
// The utils/fetcher.ts file
export function redirect(url: string) {
window.location.href = url;
}// The test beforeAll() hook
vi.resetModules();
vi.mock("../../utils/fetcher.ts", () => {
return {
redirect: vi.fn((url) => {}),
};
});// The actual test
const submit = page.getByRole("button", { name: "Register" });
await submit.click();
// This part is to import the "mocked" version of the module.
// It is of type any, so be careful with TypeScript.
const module = await vi.importMock("../../utils/fetcher.ts");
expect(module.redirect).toHaveBeenCalledWith("/login");Also needs to know that vi.unmock is also hoisted, that means even if you put it in afterAll, it will still be called right after vi.mock, and make your mocks not mocking.
What sucks? Look at this yellow stuff (I’m not happy when it’s not all green):
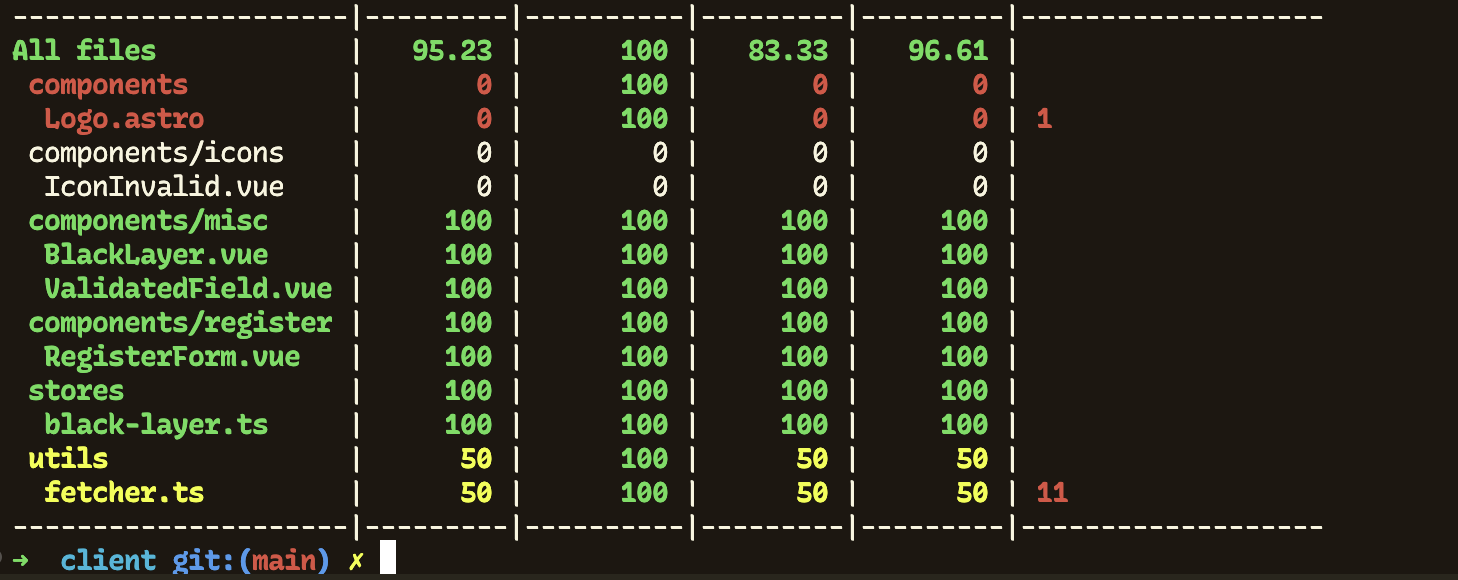
You clearly know what the uncovered line is in fetcher.ts.
Hear me rant about the process of designing my capstone project, while people that have no clues about actual designs scream at me for not doing it well enough.
I noticed a lot of clean architecture specifications don't have any demonstration on what it would look like in practice. Taking the chance of learning it in a course of Software Architecture, I think I would like to write up a demo just like so!
My first steps into my biggest project yet, a full-stack application for a comic-sharing website like Wattpad, Webtoon, etc. My first time ever setting up the server on a self-hosted VPS.